Articles
NITOS Wireless Testbed - Network Implementation Testbed Laboratory-old
NITLab Director Professor Leandros Tassiulas and its members welcome you to our Wireless Testbed, NITOS.
CERTH has developed a wireless testbed called Network Implementation Testbed using Open Source platforms (NITOS). NITOS is a testbed offered by NITLab and consists of wireless nodes based on open source software. The testbed is designed to achieve reproducibility of experimentation, while also supporting evaluation of protocols and applications in real world settings. NITOS wireless testbed has been developed as a part of the wireless facilities of the European project OneLab2.
NITOS consists of nodes based on commercial Wifi cards and Linux open source drivers. The control and management of the tesbed is done using the cOntrol and Management Framework (OMF) open-source software. NITOS testbed is deployed at the exterior of the University of Thessaly (UTH) campus building, as illustrated in figure 1.
|
|
| Figure 1. Glavani Building |
There are two servers with discrete operations to perform. The first one, the webserver, is responsible for scheduling of the testbed’s resources and its primary task is to handle users’ requests to access the testbed. It also keeps valuable information for experimentation and developing through a wiki-site. The second one, the console-server, is used to run experiments on the testbed through OMF, and to host various network services including DHCP, DNS, NTP, TFTP, PXE, Frisbee, NFS, MySQL, OML and Apache. The webserver communicates with console and they share common info and data for experiment and user handling. Indeed the webserver is the interface between the testbed and the external world, and the console server subsequently is used to execute experiments in the testbed. The console server is connected through a PoE switch which enables power switching to all nodes. Currently, the testbed supports orbit-like nodes (figure 2), diskless nodes (figure 3), and some custom made nodes. In particular, there are 10 orbit-like nodes, 15 diskless ones (ALIX 2c2 ) and 20 custom made already deployed in our campus testbed. Besides this development, NITOS has a branch for experimenting with GNU-radios, and uses 6 USRPs equipped with XCVR2450 daughterboards. This choice was driven by the fact that we aim to be as close to IEEE802.11 standards while experimenting with Software Defined Radio.
 |
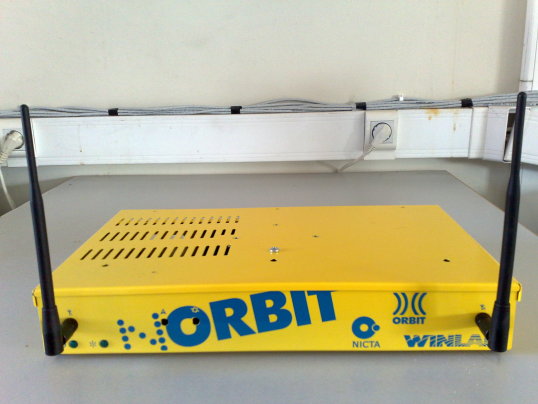 |
| Figure 2. Orbit-like nodes of NITOS testbed |
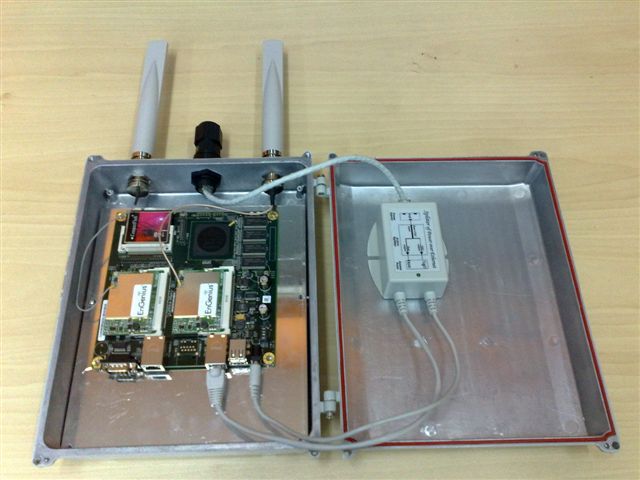 |
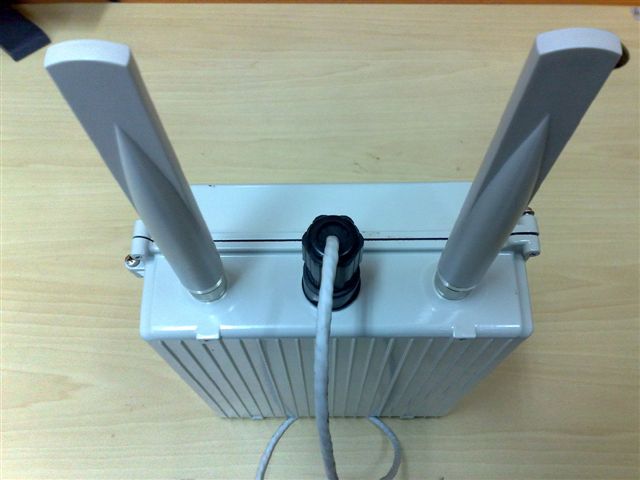 |
| Figure 3. Diskless nodes of NITOS testbed |
The diskless nodes are powered over Ethernet, however, for the orbit-like nodes that are regular powered through 220 Voltage, we use a custom made electro-mechanical disruptor controlled via the aforementioned switch and its configurable interface. All type of nodes are equipped with wireless interfaces for experimenting through the air and particularly use Wistron CM9 - mPCI Atheros 802.11a/b/g 2.4 & 5 GHz cards that also take advantage of the extensions of madwifi driver so that Click modular router features can be exploited.
The wired infrastructure of NITOS testbed deployment is used for control experimentation and resource management via OMF (cOntrol and Management Framework). OMF was initially developed by ORBIT at Rutgers University and is now maintained and extended by NICTA and CERTH. OMF simplifies the procedure of experiment definition and offers a more centralized way for deploying experiments and retrieving measurements. The NITOS platform is open to any researchers who would like to test their protocols in a real-time wireless network. They are given the opportunity to implement their protocols and study their behavior in a custom tailor-made environment. Moreover, they can access the testbed remotely and perform their experiments exploiting the beneficial slicing features that NITOS scheduler provides. They can experience a user-friendly web interface and operate with ease of use. Through NITOS scheduler a more sophisticated way of node allocation to users is achieved since multiple users have the opportunity to run their experiments at the same time sharing the testbed's resources. In addition, users are prevented from interfering with each other by selecting different frequency spectrum to operate. NITOS scheduler is an innovative testbed framework that supports a more effective way of scheduling.
NITOS, a stand-alone testbed, is constantly in the process of extending its testbed capabilities. In the long term, NITOS intends to expand its deployment with new nodes and new technologies (WIMAX, 3G) and develop new control and management modules for efficient experimentation on wireless networks. Additionally, NITOS, as part of Onelab 2, collaborates with other European institutes and intends to provide access to a unified experimental infrastructure, considering federation among different testbeds. To this end, a primary goal is to federate with the PlanetLab Europe testbed.
NITOS registered users can run their experiments real-time on the configurable wireless nodes.
For quick information about using the testbed, you can refer to tutorial.
If you already are an experienced user, you can go to scheduler to begin the node booking process.
The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Community's Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) under grant agreement n°224263-OneLab2.



