Articles
FGRE: NITOS testbed Introduction
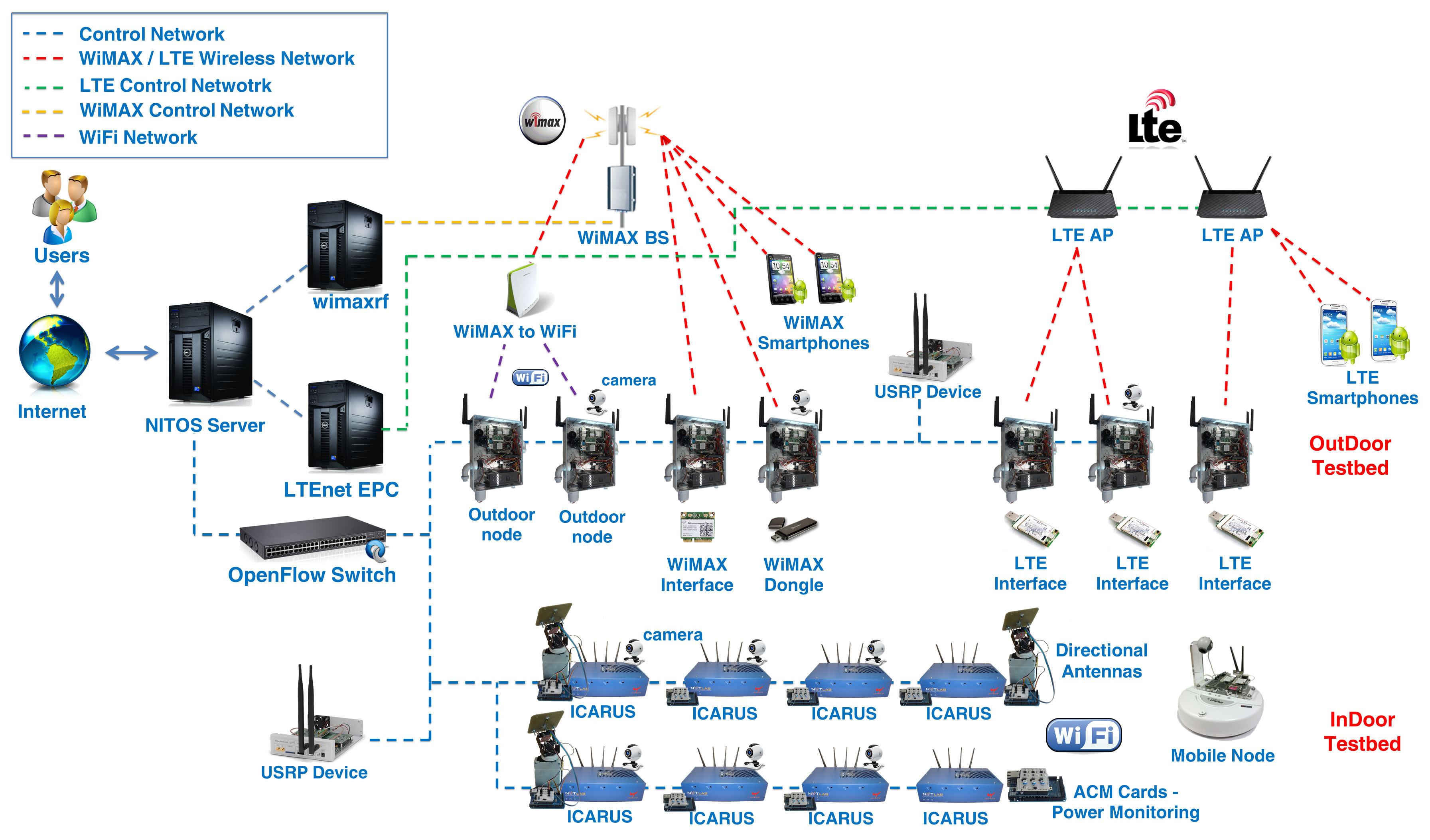
The NITOS Future Internet facility is a heterogeneous testbed that allows experimenters from all over the globe to have access on multiple cutting-edge resources, enabling the conception and experimental validation of novel protocols and ideas. The main experimental components of NITOS are:
- A wireless experimentation testbed, which consists of powerful nodes, that feature multiple wireless interfaces and allow for experimentation with heterogeneous (WiFi, Bluetooth) wireless technologies. NITOS is a meso-scale testbed, using WiMAX and LTE Base Stations. The testbed resources are deployed in three sites; 50 nodes are deployed in an interference-rich site, while 10 nodes are deployed in an RF-isolated office environment, and 50 more nodes are about to be deployed in an interference free environment.
- A software defined radio (SDR) testbed that consists of Universal Software Radio Peripheral (USRP) devices attached to the NITOS wireless nodes. USRPs allow the researcher to program a number of physical layer features (e.g. modulation), thereby enabling dedicated PHY layer or cross-layer research.
- A Software Defined Networking (SDN) testbed that consists of four OpenFlow technology enabled switches, connected to the NITOS nodes, thus enabling experimentation with switching and routing networking protocols. Experimentation using the OpenFlow technology can be combined with the wireless networking one, hence enabling the construction of more heterogeneous experimental scenarios.
- A testbed for conducting video-transmission (wired or wireless) related experimentation, which consists of high definition digital cameras, mounted on the NITOS nodes. This component can be combined with the wired (OpenFlow) and wireless testbeds mentioned above, enabling the study of video transmission over heterogeneous communication technologies.
- A distributed Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) testbed able to sense and gather environmental measurements from agricultural installations. The deployed facility consists of multiple clusters, each one comprised of wireless sensor devices and Gateway nodes, creating mesh networks utilizing the ZigBee technology. Measurements that are gathered by the sensor network are aggregated, stored and processed at a centralized cluster of servers, which controls the irrigating system. The distributed wireless sensor infrastructure is located in the agricultural installation of UTH and enables experimentation on agricultural development by sensing environmental conditions as well as controlling multiple parameters on the agricultural process.
The objective of this tutorial is that you will get an actual hands on experience with the NITOS nodes and the WiMAX Base Station.
WiMAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access) is a wireless communications standard designed to provide 30 to 40 megabit-per-second data rates.
Mobile WiMAX was a replacement candidate for cellular phone technologies such as GSM and CDMA, or can be used as an overlay to increase capacity. Fixed WiMAX is also considered as a wireless backhaul technology for 2G, 3G, and 4G networks in both developed and developing nations.
NITOS WiMAX setup is based on the Airspan Air 4GS WL-24 Base Station unit, which is configured to operate in a standalone method, without authentication.
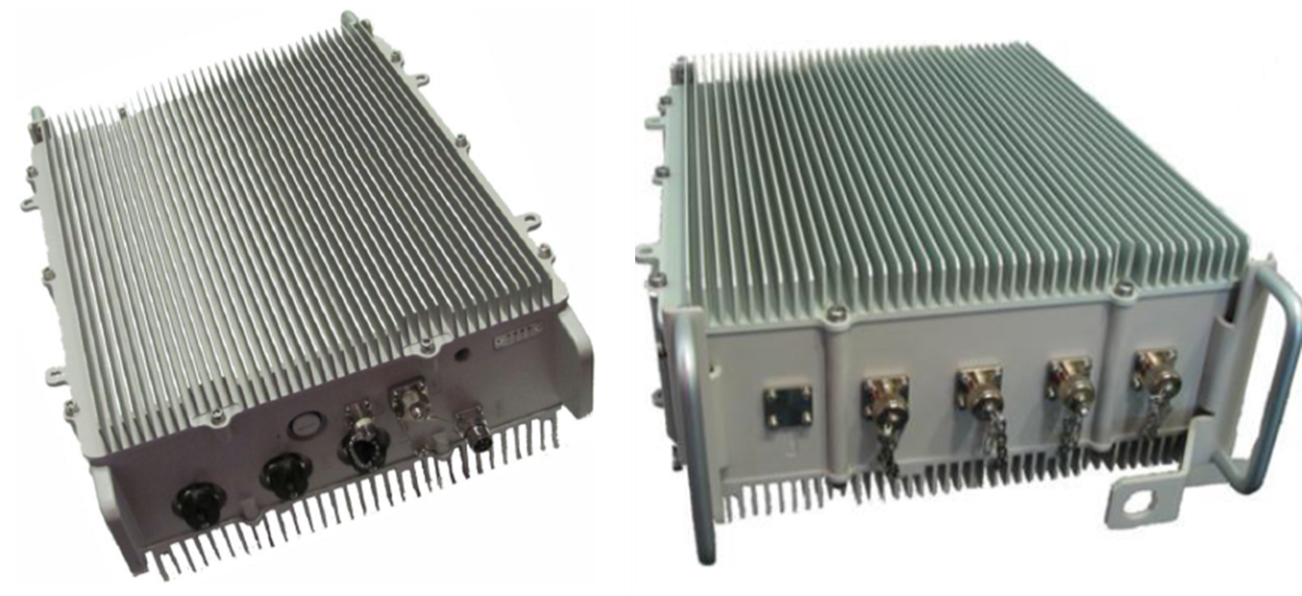

The Base Station is configured to operate using a 2590 MHz frequency using 10 MHz channel bandwidth.
The WiMAX clients that you will be using for this tutorial are the Teltonika UM6225 models which require a setup that we will explain later on.

If you want to find out more about the NITOS testbed you can visit this page.


