Articles
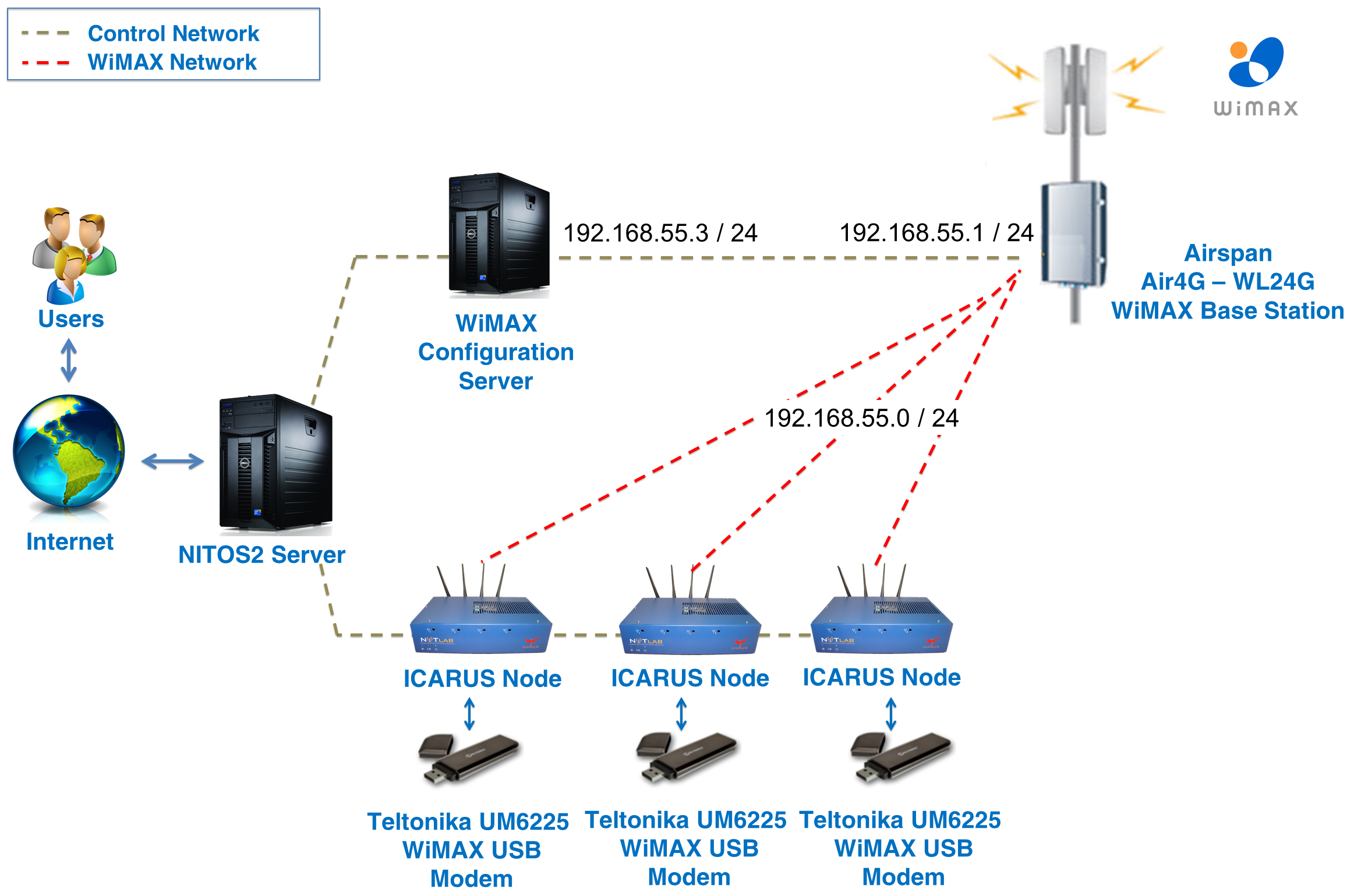
FGRE: Experimental Topology used
The topology that we are examining in this tutorial is a central Base Station unit, able to route requests from an internal WiMAX network to the internet. The process is similar to the one that takes place in your home's wireless router;
- The Base Station is using the 192.168.55.1 IP address
- Multiple clients use the 192.168.55.0/24 subnet to communicate with the Base Station
- Packets routed through the Base Station are sent over the internet through a NAT translation
However, the devices that we currently use do not allow us to interface directly the WiMAX device. If you send the following command you will all get an output similar to the following:
root@node044:~# ifconfig tel0
tel0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:1e:42:02:18:72
inet addr:192.168.0.8 Bcast:192.168.0.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::21e:42ff:fe02:1872/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:19939 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:325172 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:6477672 (6.4 MB) TX bytes:486501878 (486.5 MB)
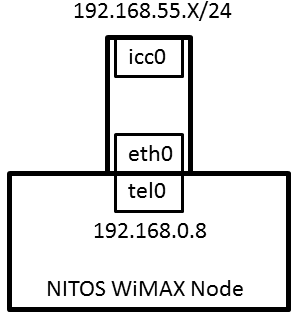
As you all observe, all the clients have the same IP address (192.168.0.8). This is ought to the architecture of the WiMAX stick which is like the following figure.
Since the WiMAX devices need a rather complex configuration in order to allow access to the WiMAX interfaces of another node, we have automated the procedure in a script. Once you have logged in a node, issue the following command:
root@node044:~# wmxfix
Now you will have to prepare the device to connect to the WiMAX network.
<< Previous Page Next Page >>


