GNU Radios
GNU radios
In NITOS testbed 6 of the Commell nodes are connected with GNU Radio boards (software defined radios), specifically USRP1 boards with XCVR2450 daughterboards (2.4-2.5 GHz and 4.9 to 5.85 GHz Dual-band Transceiver) from the Ettus Corp.
GNU Radios allow the researcher to program a number of physical layer features (e.g. modulation), thereby allowing for dedicated PHY layer or cross-layer research.
Usefull Infomation about GNU radio can be found on the official gnuradio.org site. We recommend users who intend to get involved using software defined radios to read first FAQ about Gnu Radios. It will help them resolving many queries. Also the datasheets about USRP1 and XCVR2450 daugtherboards can be found on link1 and link2 respectively.
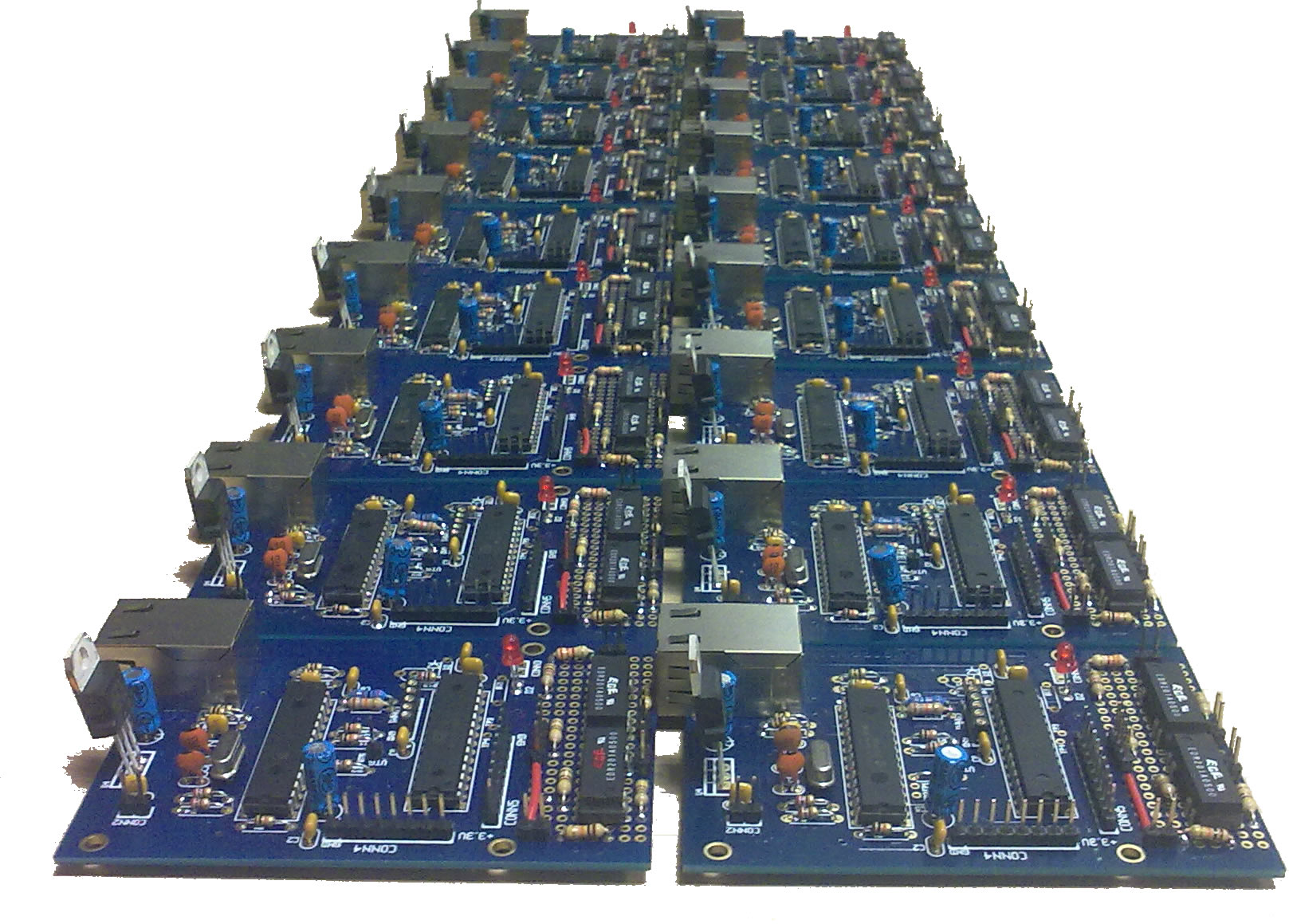
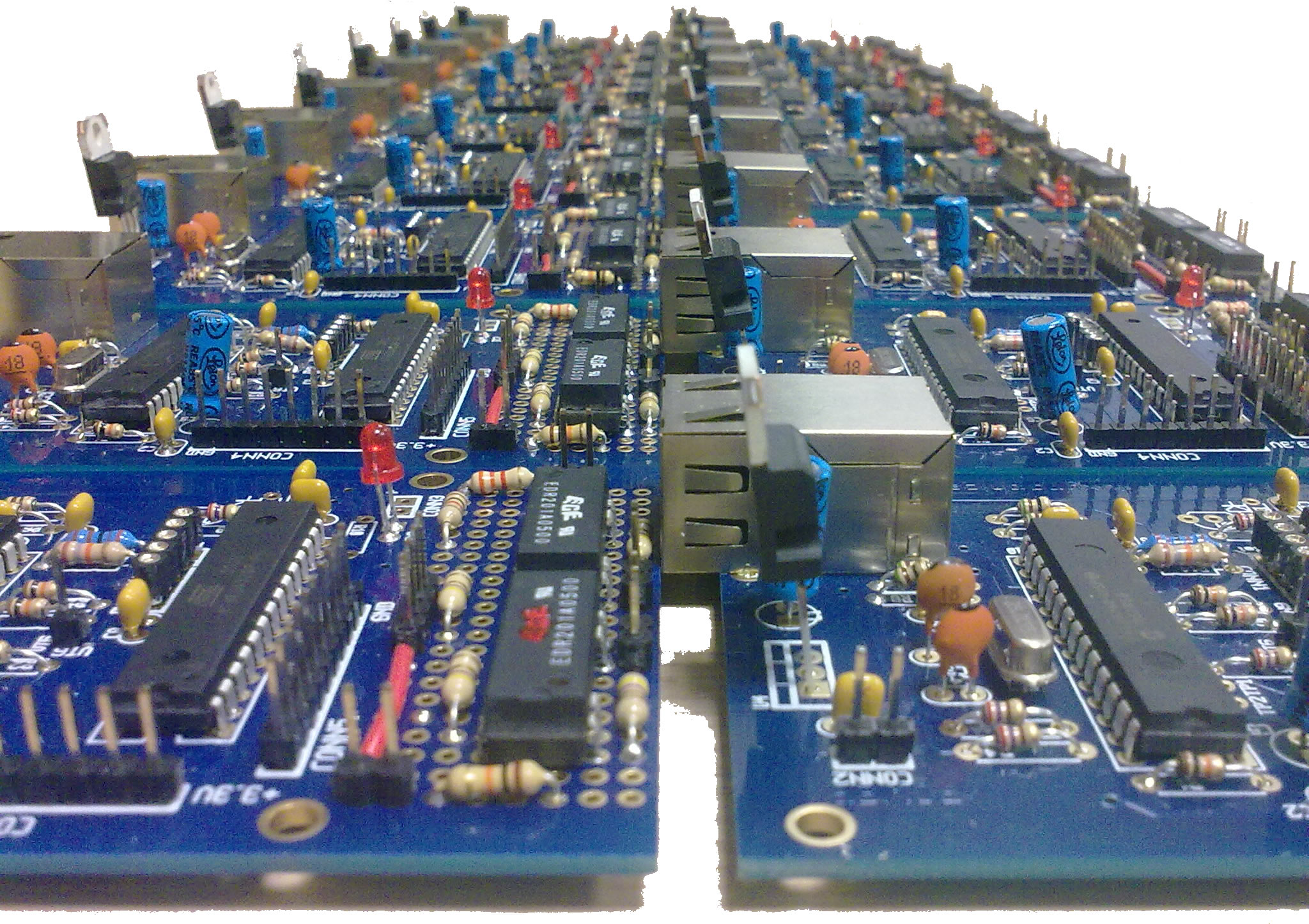
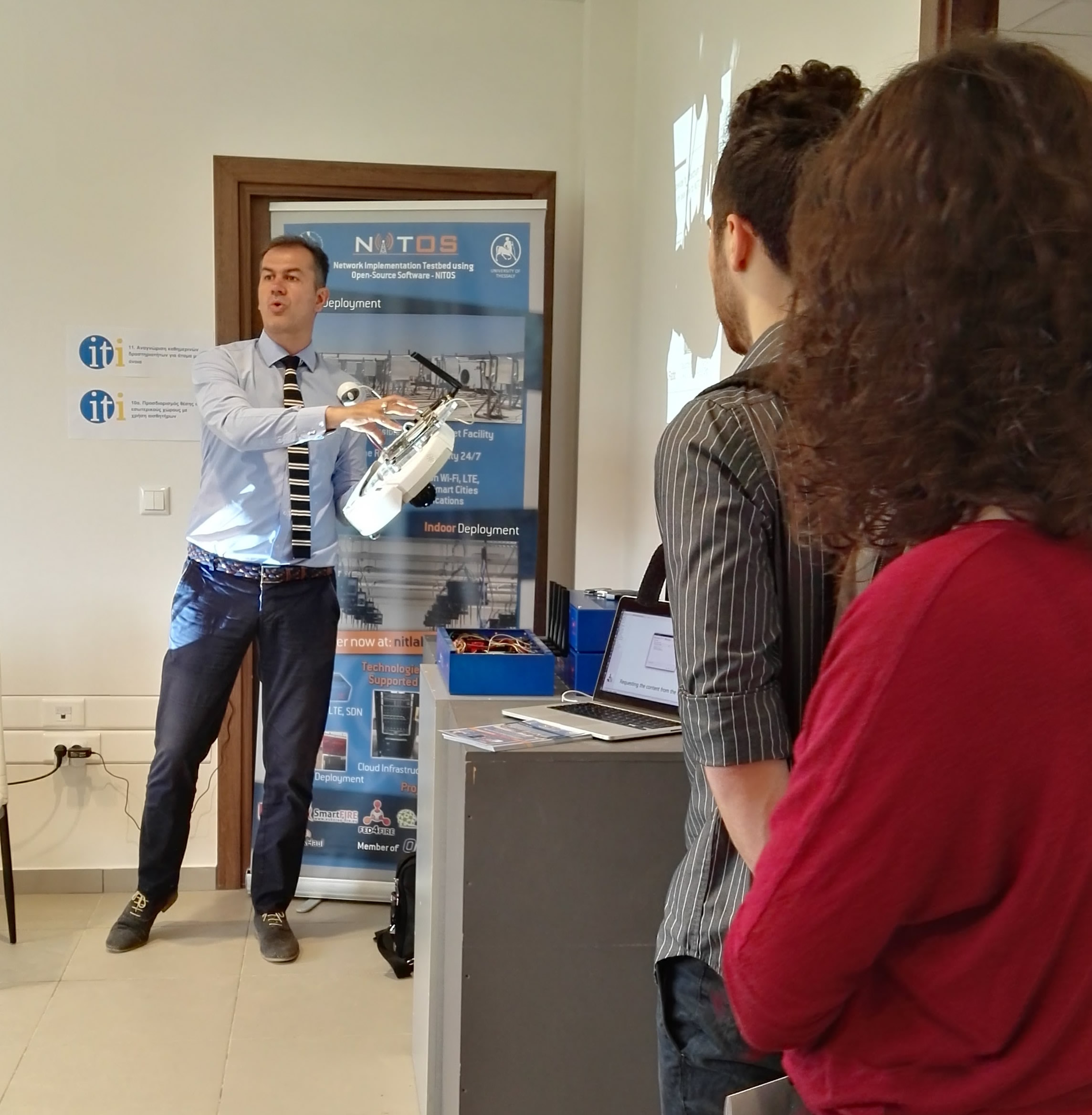
Below some photos of USRP1s deployment in NITOS testbed are illustrated.
 |
|
USRP1s assembled with XCVR2450 daugtherboards, ready to be attached on nodes |
 |
|
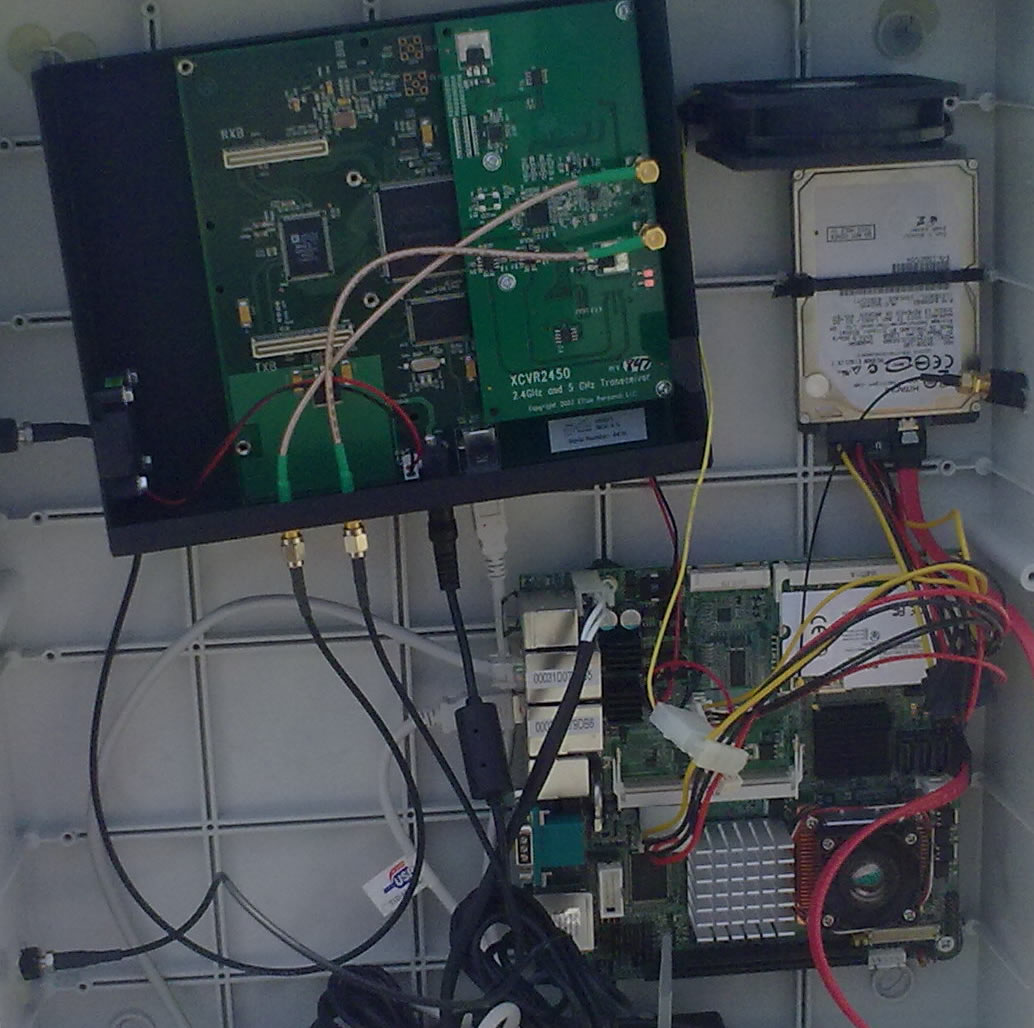
USRP1 with XCVR2450 daugtherboard, attached on a NITOS's testbed Commell Node |
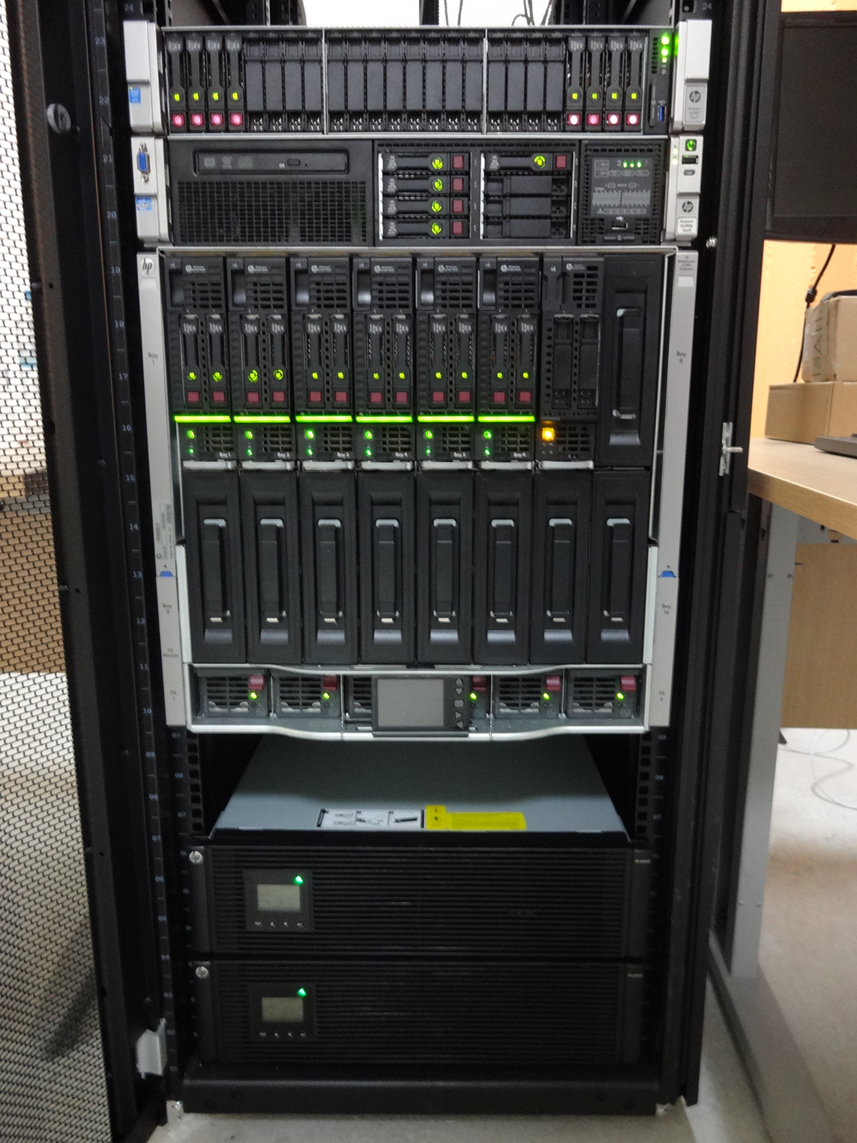



 Each blade server has
Each blade server has